How Millionaires in America’s Wealthiest Cities Structure Their Income to Build and Protect Wealth

The Income Structures of Millionaires in America’s Wealthiest Cities
Millionaires aren’t just people with a high net worth—they’re masters of structuring their income strategically. How they earn, protect, and grow their wealth varies significantly across America’s richest cities. In this article, we’ll explore how millionaires in the country’s wealthiest urban centers structure their income, the tools they use, and how local economies and tax laws shape these strategies.
What Counts as a Millionaire’s Income?
Unlike most people who rely mainly on wages, millionaires diversify their income streams to maximize growth and minimize taxes. Common sources include:
- Earned income: High salaries, bonuses, and commissions.
- Business income: Profits from LLCs, S corporations, and startups.
- Investment income: Dividends, capital gains, and stock options.
- Real estate income: Rental properties and 1031 exchanges.
- Passive income: Royalties, trust distributions, and partnerships.
Millionaire Households in America’s Wealthiest Cities

Figure 1: Millionaire households in top 10 U.S. cities by wealth.
As the chart shows, New York City leads with over 340,000 millionaire households, followed closely by San Francisco and Los Angeles. Each city’s millionaire population reflects the dominant industries and economic drivers.
How Millionaires Earn and Structure Income by City
| City | Millionaire Households | Top Income Sources | Tax Strategy Highlights | Dominant Industries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York City, NY | 340,000+ | Capital gains, hedge fund income | Use of trusts, municipal bonds | Finance, Media |
| San Francisco, CA | 300,000+ | Stock options, RSUs | Grantor trusts, LLCs | Tech, Startups |
| Los Angeles, CA | 270,000+ | Real estate, entertainment royalties | LLCs, 1031 exchanges | Entertainment, Real Estate |
| Miami, FL | 230,000+ | Crypto, real estate, offshore income | No state income tax, offshore trusts | Finance, Crypto |
| Dallas, TX | 180,000+ | Oil/gas royalties, small business income | S corps, 401(k) strategies | Energy, Tech |
| Boston, MA | 170,000+ | Salaries, biotech equity | Donor-advised funds | Education, Biotech |
| Chicago, IL | 165,000+ | Business income, municipal bonds | Life insurance wrappers | Healthcare, Finance |
| Seattle, WA | 150,000+ | Tech stock compensation | Deferred compensation plans | Tech, Aerospace |
| Washington, DC | 140,000+ | Lobbying income, federal consulting | Asset protection trusts | Government, Legal |
| Houston, TX | 130,000+ | Real estate, energy royalties | Tax-deferred real estate deals | Energy, Real Estate |
Typical Income Sources by City
New York City, NY

San Francisco, CA

Miami, FL
Tools Millionaires Use to Structure Their Income
- LLCs and holding companies to protect assets and optimize taxes
- 1031 exchanges for deferring capital gains on real estate
- Trusts (revocable, irrevocable, offshore) for income sheltering and estate planning
- Charitable foundations and donor-advised funds for tax benefits and legacy
- Retirement accounts like SEP IRAs and Solo 401(k)s
- Life insurance policies used for tax sheltering and wealth transfer
How Location Shapes Income Strategy
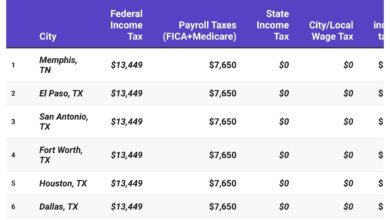
No Income Tax States (FL, TX, WA): Focus on real estate and capital gains with tax-free state income.
High-Tax States (NY, CA): Use trusts, municipal bonds, deferred compensation, and charitable giving to reduce taxable income.
Industry Clusters: Tech hubs favor stock compensation and equity; finance hubs rely on capital gains and business income.
Conclusion
Millionaires in America’s wealthiest cities do more than earn high incomes — they strategically build, protect, and diversify their wealth in ways that leverage their city’s unique economic landscape and tax environment. Understanding these structures offers valuable lessons for anyone interested in financial growth and sustainability.