How Much You Need to Earn to Afford a Home in the 50 Biggest U.S. Cities and the Priciest Housing Markets

According to a recent analysis by mortgage analytics firm HSH, homeownership in the largest U.S. cities has become increasingly unattainable for all but the wealthiest residents.
In San Jose, California, a household must earn $463,887 annually to afford a median-priced home, making it the most expensive city among the 50 largest in the U.S. This estimate assumes a 20% down payment, a mortgage rate of 7.16% for borrowers with good or excellent credit, and that no more than 28% of gross income goes toward housing costs.
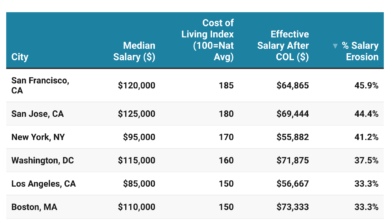
In the 50 largest U.S. cities, the average income required to afford mortgage payments — including principal, interest, property taxes, and homeowners insurance — is $104,339. That’s significantly higher than the national median household income of $74,580, according to U.S. Census data.
It’s no surprise that the largest U.S. cities require the highest incomes to afford a home. Strong demand for housing is fueled by abundant job opportunities, especially in well-paying sectors like technology, finance, and health care.
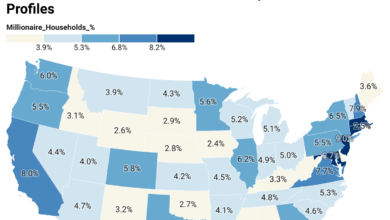
Another major factor is the longstanding shortage of homes, which is particularly severe in California. This housing crunch helps explain why median home prices in cities like San Jose are roughly double the national median of $412,300, according to U.S. Census data.
Here’s a look at the 50 largest metro areas, ranked by how much income is required to afford a median-priced home in each market.