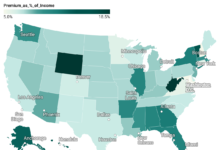
The Average Cost of Car Insurance by U.S. States

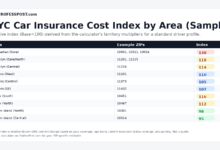
In 2023, the average yearly car insurance cost across the nation was $3,017, equivalent to $251 per month. Michigan recorded the highest annual premium at $5,766, translating to $480 monthly.
In 2023, the average annual cost of car insurance in the United States stood at $3,017, roughly equivalent to $251 per month. This sum exceeds the average American expenditure on clothing and represents 4% of the median income in the country.
It’s important to note that car insurance rates fluctuate based on location, provider, and individual factors such as driving history and credit score. Periodically comparing rates from various insurers can help identify potential cost-saving opportunities.
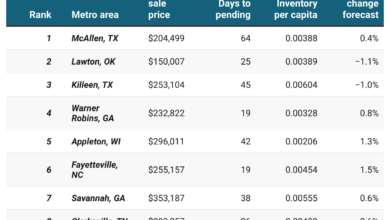
The choice of car insurance coverage greatly influences the policy’s cost. Minimum coverage, mandated by states, is notably more affordable, averaging $787 annually or around $66 monthly in 2023. In contrast, comprehensive coverage comes at a higher price, averaging $3,296 annually or approximately $275 per month.
Basic auto insurance typically includes liability coverage, encompassing bodily injury and property damage liability to address costs from injuries or property damage in accidents. Standard coverage may also extend to uninsured/underinsured motorist, comprehensive, collision, medical payment, and personal injury protection.
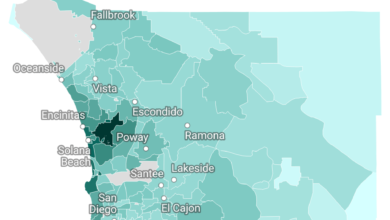
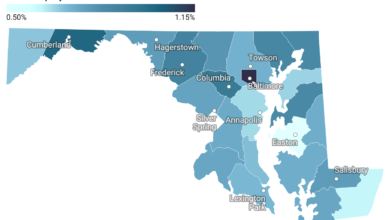
Car insurance in the Mid-Atlantic often comes with a higher price tag due to the region’s requirement for elevated minimum liability coverage. Additionally, some states mandate additional coverage like personal injury protection and uninsured motorist coverage, contributing to an overall increase in the average car insurance premium in these areas.
How can one reduce their auto insurance premium?
To secure a more favorable car insurance rate, it’s crucial to grasp the factors influencing the pricing of auto insurance policies. Companies typically evaluate these key elements using their proprietary insurance scoring systems:
Driving Record: Individuals with a clean history generally enjoy lower rates, while new drivers or those with major infractions like accidents, DUIs, or speeding tickets often face higher premiums.
Driving Frequency: The more you drive, the higher your insurance cost may be, reflecting an increased risk of accidents associated with frequent driving.
Location: Residing in areas with elevated rates of theft or accidents can lead to higher auto insurance costs. Regions prone to severe weather, such as hailstorms damaging cars, may also experience more expensive policies.
Gender: Traditionally, women have been considered safer drivers, potentially translating into better car insurance rates for female policyholders.
Automobile Model: The cost of insurance is influenced by the type of vehicle you drive. More expensive cars generally incur higher insurance premiums, while vehicles equipped with certain safety features may qualify for discounts.