Which States Don’t Tax Some or All Retirement Income?
States tax retirement income differently, so your location impacts your budget. Some tax pensions or IRAs, while others offer broad exemptions or no income tax.
Most types of retirement income can be taxed at the federal level, including Social Security benefits, pension payments, and withdrawals from traditional IRA and 401(k) accounts. The main exception is qualified withdrawals from Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s. Because Roth contributions are made with after-tax dollars, both the contributions and any earnings can be withdrawn tax-free once you’re at least 59½ and have met the five-year rule.
State taxation, however, is far less uniform. A handful of states don’t levy any income tax, which means all retirement income is automatically tax-free locally. Many states also exclude Social Security from taxation, and some go further by exempting pensions or retirement-account withdrawals. Still, most states take a mixed approach, taxing certain forms of retirement income while offering breaks on others.
Only eight states tax Social Security to any degree: Colorado, Connecticut, Minnesota, Montana, New Mexico, Rhode Island, Utah, and Vermont. In all other states, Social Security benefits are exempt, though retirees may still owe state income tax on pensions, 401(k) withdrawals, IRA distributions, and other income once it passes certain thresholds.
9 States That Don’t Tax Any Income at All
Nine U.S. states do not levy any income tax on individuals. Eight of them — Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming — avoid taxing wages, salaries, dividends, interest, and all other forms of income.
New Hampshire is the ninth. It does not tax wages, salaries, pension payments, or retirement account withdrawals. Historically, it taxed interest and dividends, but those taxes end in 2025. When that happens, New Hampshire will fully join the other no-income-tax states.
Because these states don’t charge income tax, they also do not tax Social Security benefits, pension income, or withdrawals from retirement accounts. That means retirees living in these states face no state-level tax burden on any of their retirement income, aside from New Hampshire’s temporary interest and dividend taxes.
Every other state handles retirement income differently. Some tax all retirement income, including Social Security, while others exempt part or all of it depending on the type of income and the taxpayer’s situation.
States That Exempt Some or All Retirement Income
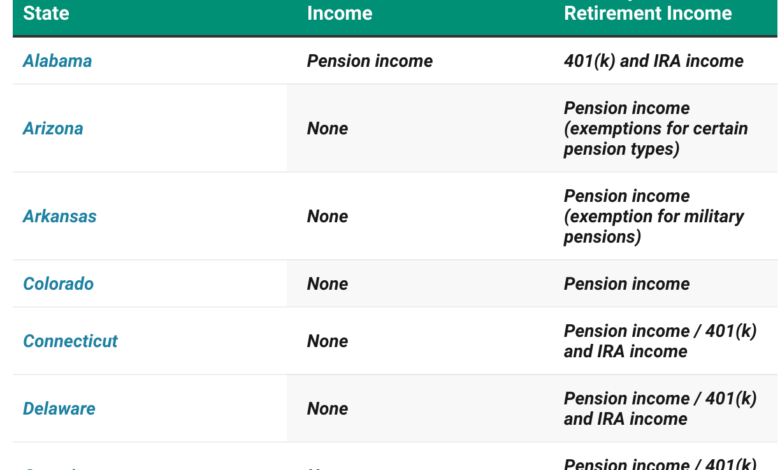
A total of 32 states offer partial tax relief on retirement income, either by exempting certain types of pension or retirement-account withdrawals or by taxing only a portion of them.
Some states not on the “no-tax” list still treat retirees favorably. Georgia exempts Social Security benefits and offers a large retirement-income deduction—$35,000 to $65,000 per person depending on age. Pennsylvania also exempts Social Security, IRA and 401(k) withdrawals, and pension income for residents over 60.
Overall, retirement-income taxation varies widely, often relying on income limits or age requirements. It’s also constantly changing. For example, New Hampshire is phasing out its tax on interest and dividends, which will drop to zero by 2025.